March 10, 2013
Category: microsoft, rds-2012, virtualisation
Tags: certificate-authority, gateway-farms, group-policy, internal-servers, public-key-certificate, rds, remote-desktop-services, remote-desktop-services-2012, server-certificates, single-sign, wild-card
Configuring RDS 2012 Certificates and SSO
Applying Certificates to a RDS Deployment
Once you have installed RDS, you will need to configure the RD Certificates for RDS to function properly.
The RDS Certificates for authentication purposes (SSO, external access, Session host connections etc).
Self assigned certificates s are no good for a production environment should only be used for LAB's, UAT, and POC.
If certificates are not configured or incorrectly configured you will see issues when using RDS. External access is one of the biggest issues users face, especially with ".local" internal domains when accessing RDS externally. If you use a self assigned certificate for the RD Gateway, you will need to export from the RD Gateway and import the certificate to all clients that what to access the RD Gateway.
Recommendations:
- Use a Wild Card certificate which simplifies the deployment .
- Use SAN Certificates if you don't want to pay Wild Card prices.
- individual certificates are great for single instance deployments or for low budget deployments. managing multiple certificates can get messy.
In this example I will use self assigned certificates that show un-trusted.
In the real world all certificates should show as Trusted.
Please see the following Link http://www.cacert.org or Commodo for Free certificates. I would recommend purchasing certificates for production environments.
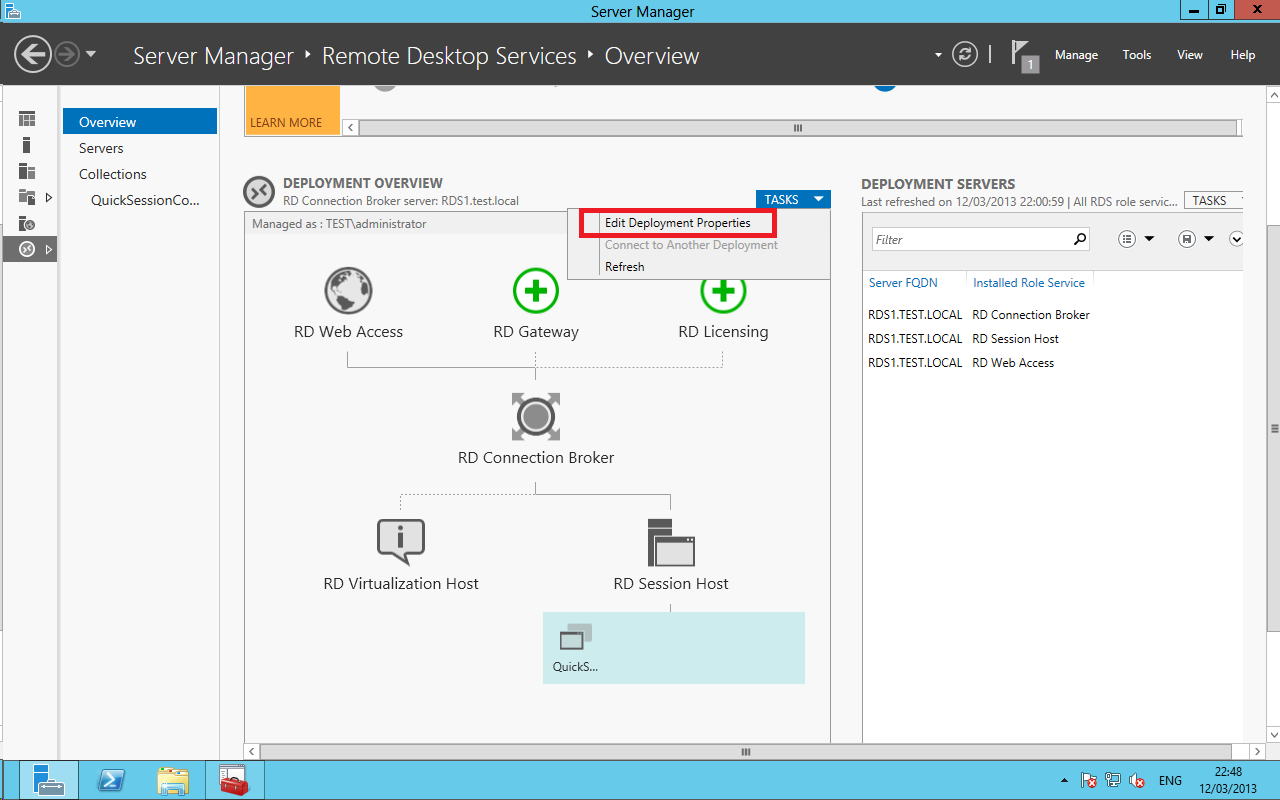
On the overview screen of Remote Desktop Services, select Tasks > Edit Deployment Properties
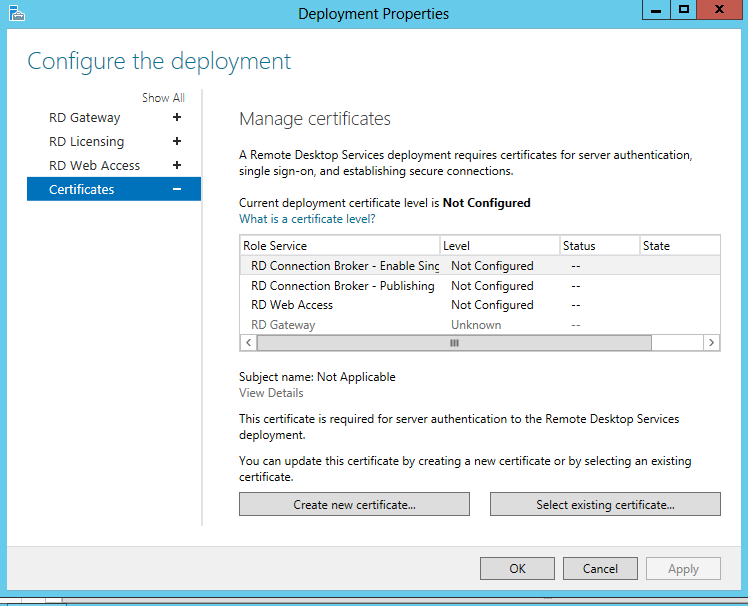
In this demo, we will be creating self assigned certificates. As mentioned before, in the real world you would use trusted certificates and use the option select existing certificate...
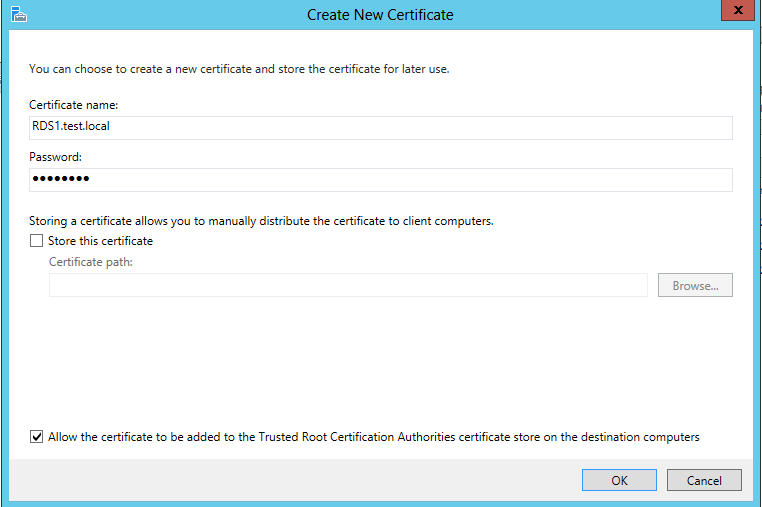
Creating a self assigned certificate using the server FQDN and setting a password
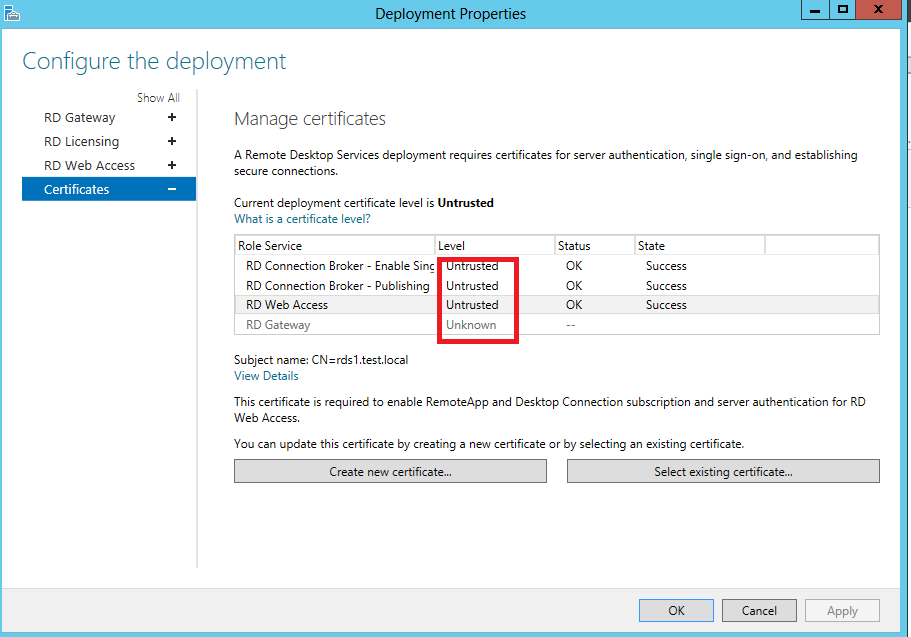
As you can see from this screenshot, All certificates are not trusted as they are self assigned. To change this to trusted, you would need to use a third party certificate (Public CA certificate) or a internal Root CA to connect.
Using a internal CA also has limitations as you would need to use domain joined clients or import the internal ca certificates to the external client.
When importing Certificates from a verified Public Certificate Authority /Internal CA you will see that the level will change from untrusted to trusted.
Certificate Mismatches
As mentioned earlier, lots of users have issues when deploying RDS to a ".local" Domain. When publishing RDS externally, you will see a certificate mismatch as the internal server FQDN's/IP address's will show externally during the connection process to RemoteApps or RemoteDesktops.
There are a number of ways to resolve this including creating a custom RDP property that redirects to a alternative name. This is a great way to resolve a single instance deployment in a ".local" domain.
Set-RDSessionCollectionConfiguration –CollectionName QuickSessionCollection -CustomRdpProperty “use redirection server name:i:1 `n alternate full address:s:remote.domain.com”
There is also a way of changing the client access address of the connection broker using a WMI script provided below.
Change published FQDN for Server 2012 or 2012 R2 RDS Deployment
The Script has been generously provided by "TP". Please note that there are issues using RD Web feed after using this to change the client access name. RDS looks for a RDCB farm during the connection process and then fails. You can review these errors in the event logs.
Bypassing RDP Authentication
Older versions of windows connected to the computer before checking credentials, RDS now checks credentials before connecting. The following custom RDP Property is not to be used with out security considerations, but if you want to turn off warning or alerts for use in a POC/LAB/UAT Environment then its perfectly fine to get round warnings and connection issues. I do not recommend that you use this in a production environment.
Set-RDSessionCollectionConfiguration –CollectionName QuickSessionCollection -CustomRdpProperty “authentication level:i:0”
see the following link for more details:
Creating and Deploying Certificates, the PowerShell Way
ensure that you have imported the Remote Desktop PowerShell Module and Set the password for the certificate
Import-module Remotedesktop $Password = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "RDS%%G0d" -AsPlainText -Force
You will then be able to create the certificates:
To Import a certificate you would use Get-RDCertificate
To Create a certificate you would use New-RDCertificate
To find out which certificates are associated with RDS roles, you would use Get-RDCertificate
the following commands are used for creating self assigned certificates.
#RDPublishing Certificate
New-RDCertificate -Role RDPublishing -DnsName "<Server Name>" -Password $Password -ConnectionBroker "<Connection Broker Name>"
#RDWebAccess Certificate
New-RDCertificate -Role RDWebAccess -DnsName "<Server Name>" -Password $Password -ConnectionBroker "<Connection Broker Name>"
#RDRedirector Certificate
New-RDCertificate -Role RDRedirector -DnsName "<Server Name>" -Password $Password -ConnectionBroker "<Connection Broker Name>"
#RDGateway Certificate
New-RDCertificate -Role RDGateway -DnsName "<Server Name>" -Password $Password -ConnectionBroker "<Connection Broker Name>"
Configuring RDSH Server Certificates
Before configuring RDSH Servers you will see a warning stating that the certificate is untrusted.
This is because the configuration data for RDSH is stored in the WMI, Win32_TSGeneralSetting class in WMI in the rootcimv2TerminalServices namespace. You will need to change the certificate from default using the following commands.
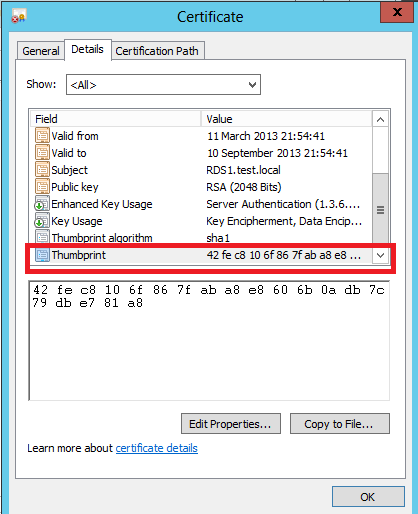
Firstly, You will need to find the certificate thumbprint.
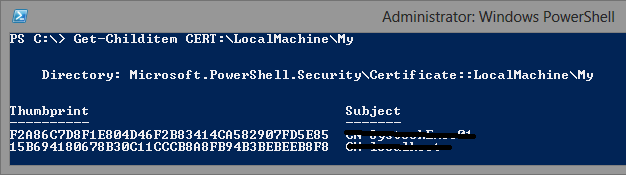
You can also use PowerShell to find the Thumbprint:
Get-Childitem Cert:\LocalMachine\My
Run one of the following cmds to apply the new certificate to the Win32_TSGeneralSetting:
wmic /namespace:\\\\root\\CIMV2\\TerminalServices PATH Win32\_TSGeneralSetting Set SSLCertificateSHA1Hash="Thumbprint"
PowerShell Cmd:
$path = (Get-WmiObject -class "Win32\_TSGeneralSetting" -Namespace rootcimv2terminalservices -Filter "TerminalName='RDP-tcp'").\_\_path Set-WmiInstance -Path $path -argument @{SSLCertificateSHA1Hash="THUMBPRINT"}
RDS 2012 RDSH Certificate deployment script
You can also download the script above which simplifies the process.
Credentials Delegation Group Policy setting
Single Sign On can now use the logged-on user credentials of a intranet user who is subscribed to a RemoteApp and Desktop Connection Feed. To enable SSO, you need to add the FQDN of the RD Connection Broker /Farm / Wild Card with the 'TERMSRV/ Prefix" to the credentials delegation Group Policy setting.
This policy is located in Computer Configuration -> Policies ->Administrative Templates -> System -> Credential Delegation -> Allow delegation defaults credential.
I would recommend making this GPO a domain assigned policy.
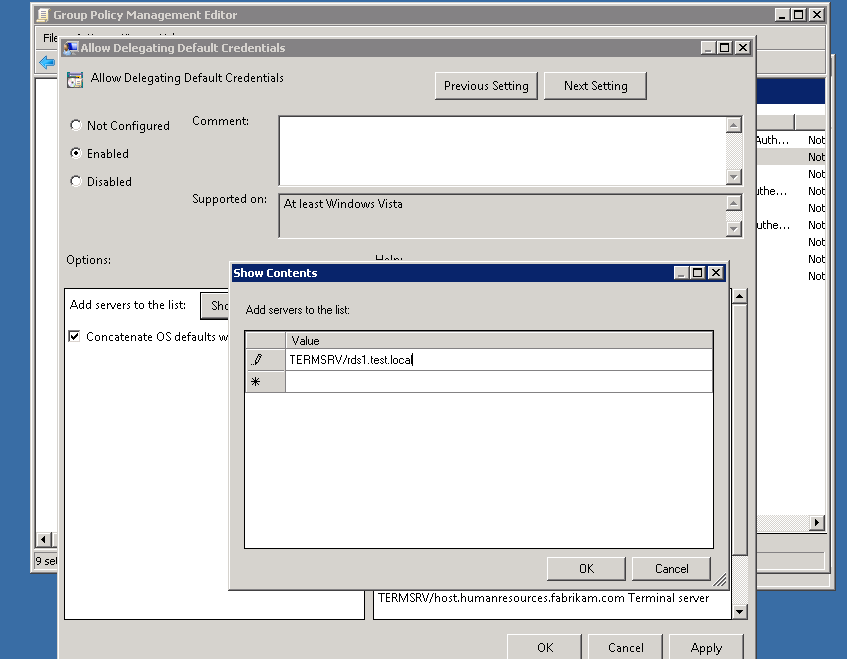
To achieve Single Sign-On you would need to complete the following steps:
- Install and configure SSL certificates on RD Gateway, RD Web and RD Connection Broker servers.
- Enable Web SSO on RDWeb Access servers
- Configure the group policy for credentials delegation as shown above.
- Add the Certificates created above to the .rdp trusted publishers using GPO:(Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Connection Client). Specify SHA1 thumbprints of certificates representing RDP publishers
Once completed, users will be able to connect to desktops and RemoteApp's with out re-entering their password.
