September 18, 2013
Category: kemp-tech, office-365, virtualisation, windows-server-2012
Tags: active-directory, adfs, afds, afds-proxy, dirsync, domain-name-system, federated-services, hypertext-transfer-protocol, ip-address, kemp, load-balancing, microsoft-office-365, on-premise, proxy-server, windows-azure
Load Balance AFDS and ADFS Proxy in Windows Azure with KEMP
This article will show you how to load balance ADFS and ADFS proxy servers in Windows Azure using my favourite Load Balancer "KEMP".
KEMP are one of the first vendors to release a layer 7 load balancer on the Windows Azure Platform. You can check out the Azure VLM Specs at http://kemptechnologies.com/uk/load-balancer-for-azure
At the time of writing this article: the Azure VLM is free with free email support.
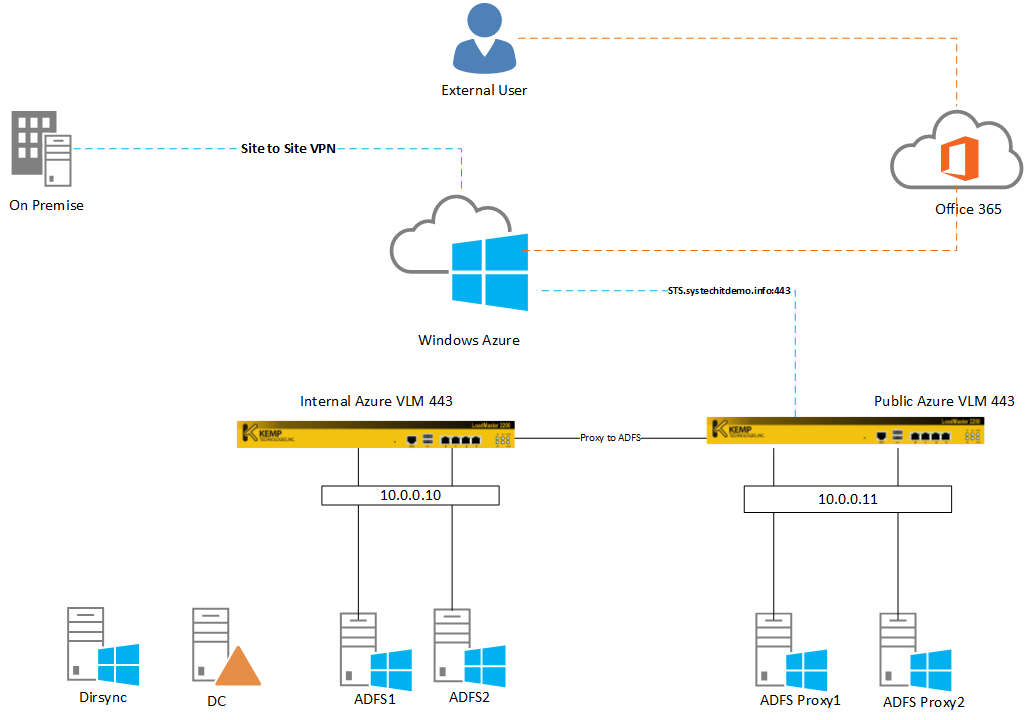
My Lab consists of:
2x ADFS Servers 2x ADFS Proxy Servers 1x DC 1x DirSync 2X Azure VLM's
[ ](
](
Before I go into the configuration side of things, I wanted to explain the diagram.
I have a site to site VPN linking my Windows Azure platform to my on premise datacentre. I have a DC in Windows Azure which replicates to and from the on premise DC. The big question ... Why deploy Office 365 federation services to Windows Azure ? There are pros and cons for deploying ADFS to Windows Azure. A Popular answer: If you have a on premise outage, your external users will not be able to sign into Office 365 as there will be no access to the Federated services. Windows Azure provides the ability for users to still sign in if there is a outage on premise.
Dirsync has been configured and is a crucial part of the configuration, all user accounts need to be synced with Windows Azure's Active Directory for ADFS to work.
I have used two KEMP Azure VLM's because you can only have one IP address per Azure VLM. Only one HTTPS 443 Endpoint per cloud service is possible so I had to create a seperate cloud service for the internal Azure VLM. This allows you to load balance both ADFS and ADFS proxy Services.
The ADFS Proxy Servers are none Domain Joined and will be public facing.
The configuration:
- Deploy two Azure VLM'S, one in the office 365 cloud service and one in a separate cloud ensure both VLM'S have HTTPS endpoints configured. I configured the internal VLM to be in a separate cloud. For details on how to deploy the Azure VLM's please see the following link http://ryanmangansitblog.wordpress.com/2013/08/24/kemp-loadmaster-in-windows-azure/
- Import the ADFS Certificate to both VLM's.
- Once you have created the VLM's add the internal VLM's IP address to both ADFS Proxy Servers.
[ ](
](
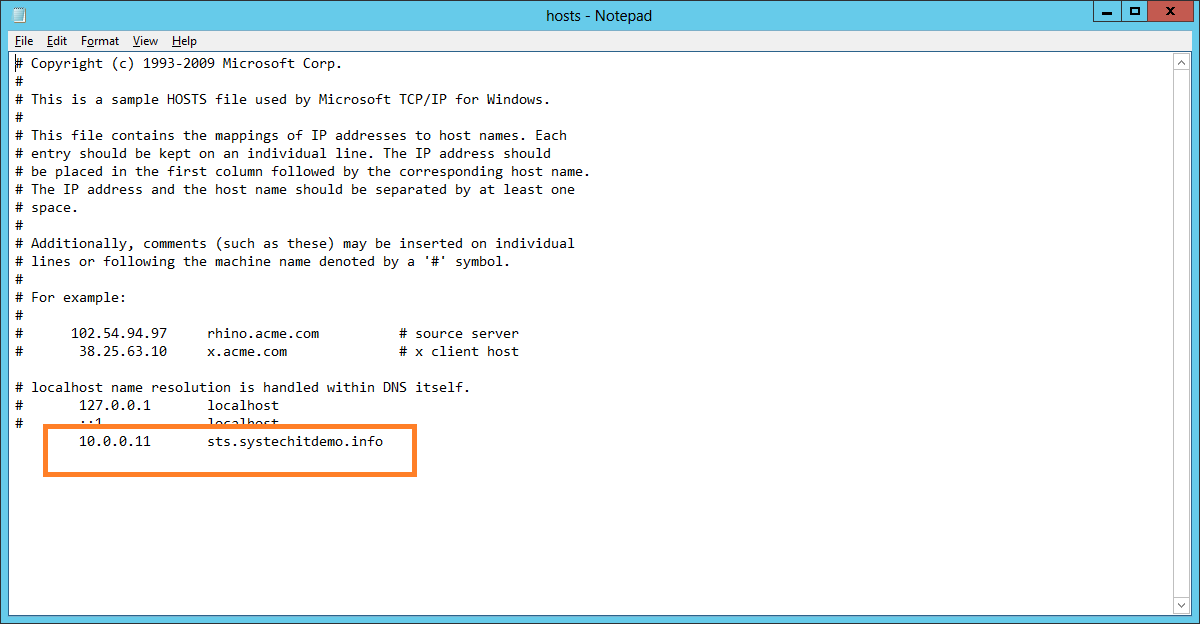
- My DNS is a split brain configuration so I added the internal ADFS Farm IP to the systechitdemo.info zone.
- Copy the ADFS Proxy Cloud DNS name and create a CName on your external DNS pointing towards "sts.domain.com"
[ ](
](
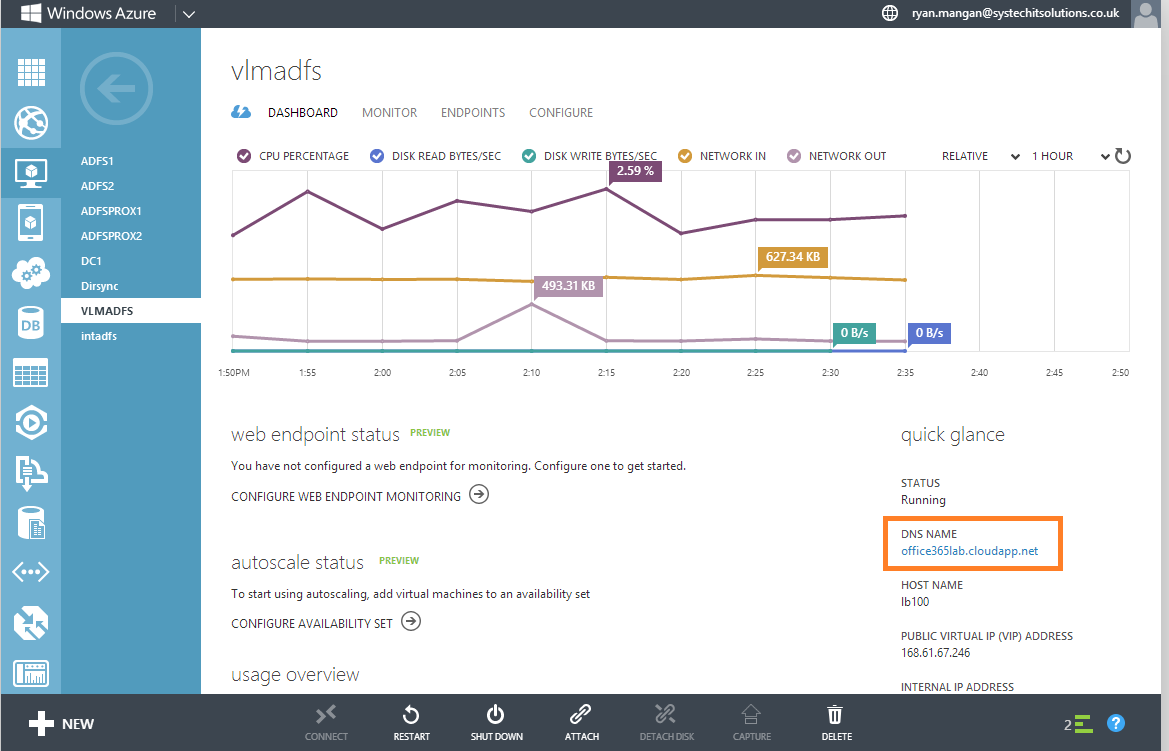
The DNS name is located in the virtual machine's dashboard under quick glance.
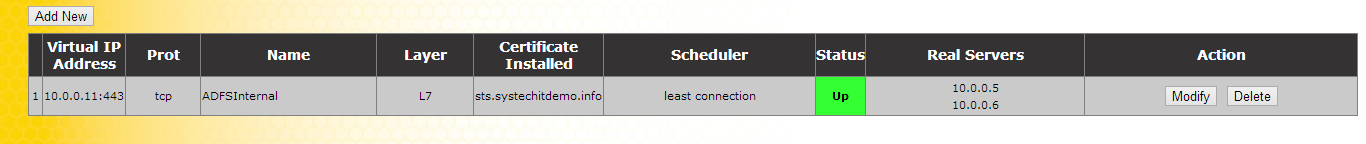
Configuring the ADFS VLM
Create a new Virtual Service:
[ ](
](
Basic properties:
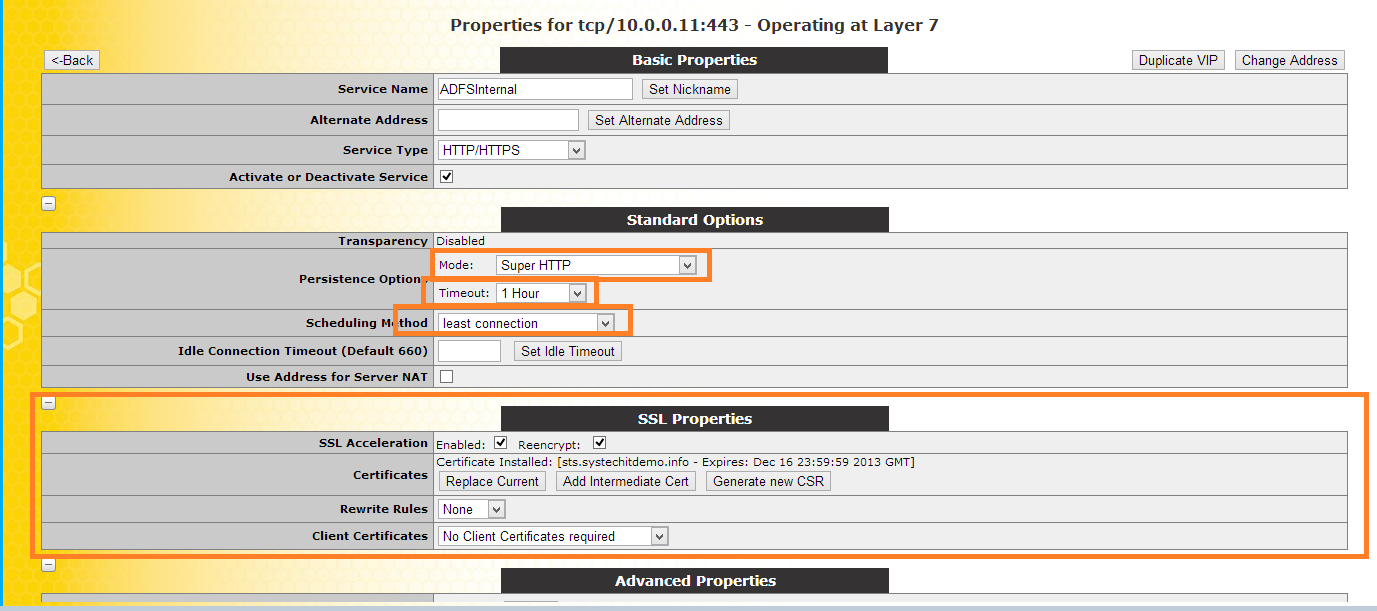
Give it a service Name: "ADFS Internal"
Enable SSL
Standard options:
Persistance options:
Mode: Supper HTTP
Timeout: 1hour
Scheduling method: least connection
SSL Properties:
SSL Acceleration: Reencrypt
Add the certificate to the service
Real Servers:
[ ](
](
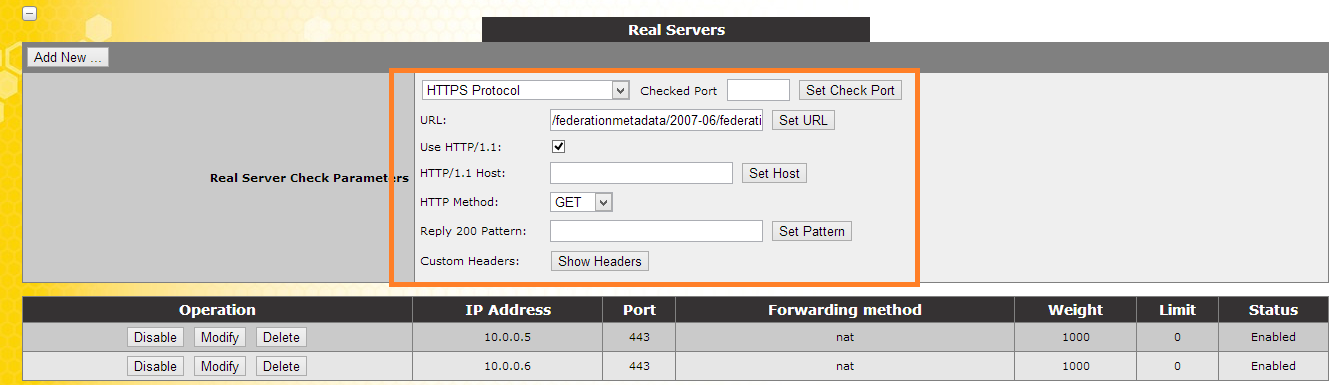
Under Real Server Check Parameters:
add the following URL and click set URL: /federationmetadata/2007-06/federationmetadata.xml
tick the Use HTTP/1.1
and change the HTTP Method to GET
Then add the ADFS server IP address's
[ ](
](
Test access to the AD FS Internal Farm by navigating to https://"sts.domain.com"/ADFS/ls/idpininitiatedsignon.aspx and following the instructions to log in.
Configuring the ADFS Proxy FARM:
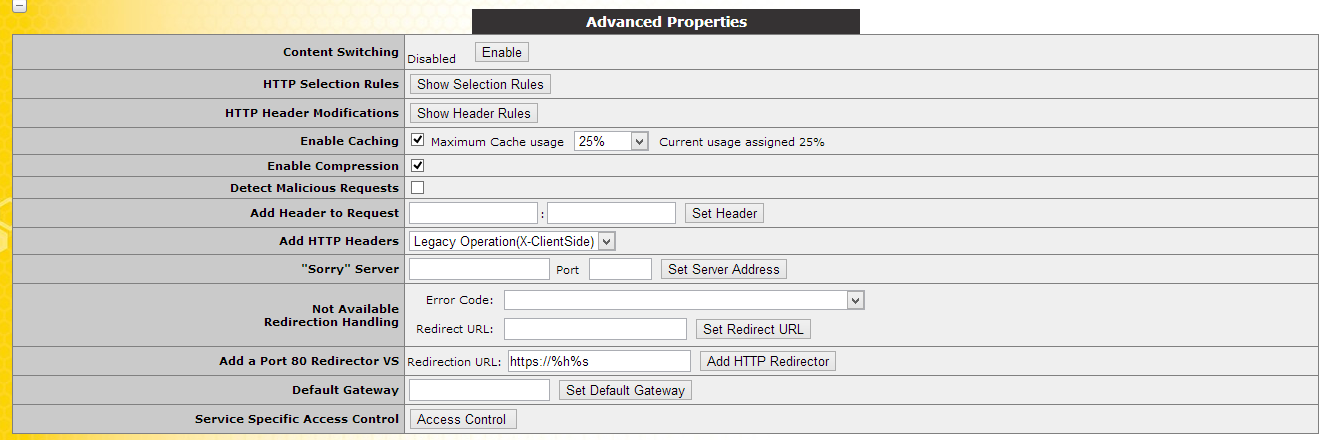
The ADFS Proxy Configuration is the same as ADFS but with a few differences.
[ ](
](
Enable Caching and set the usage to 25%
Enable Compression
[ ](
](
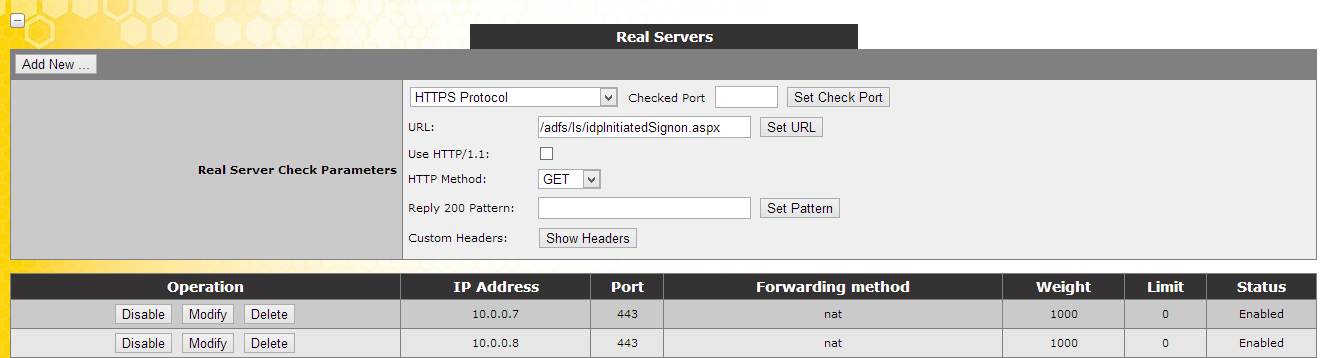
Set the URL to /adfs/ls/idpInitiatedSignon.aspx and click set URL.
Set the HTTP Method to GET.
Final test:
[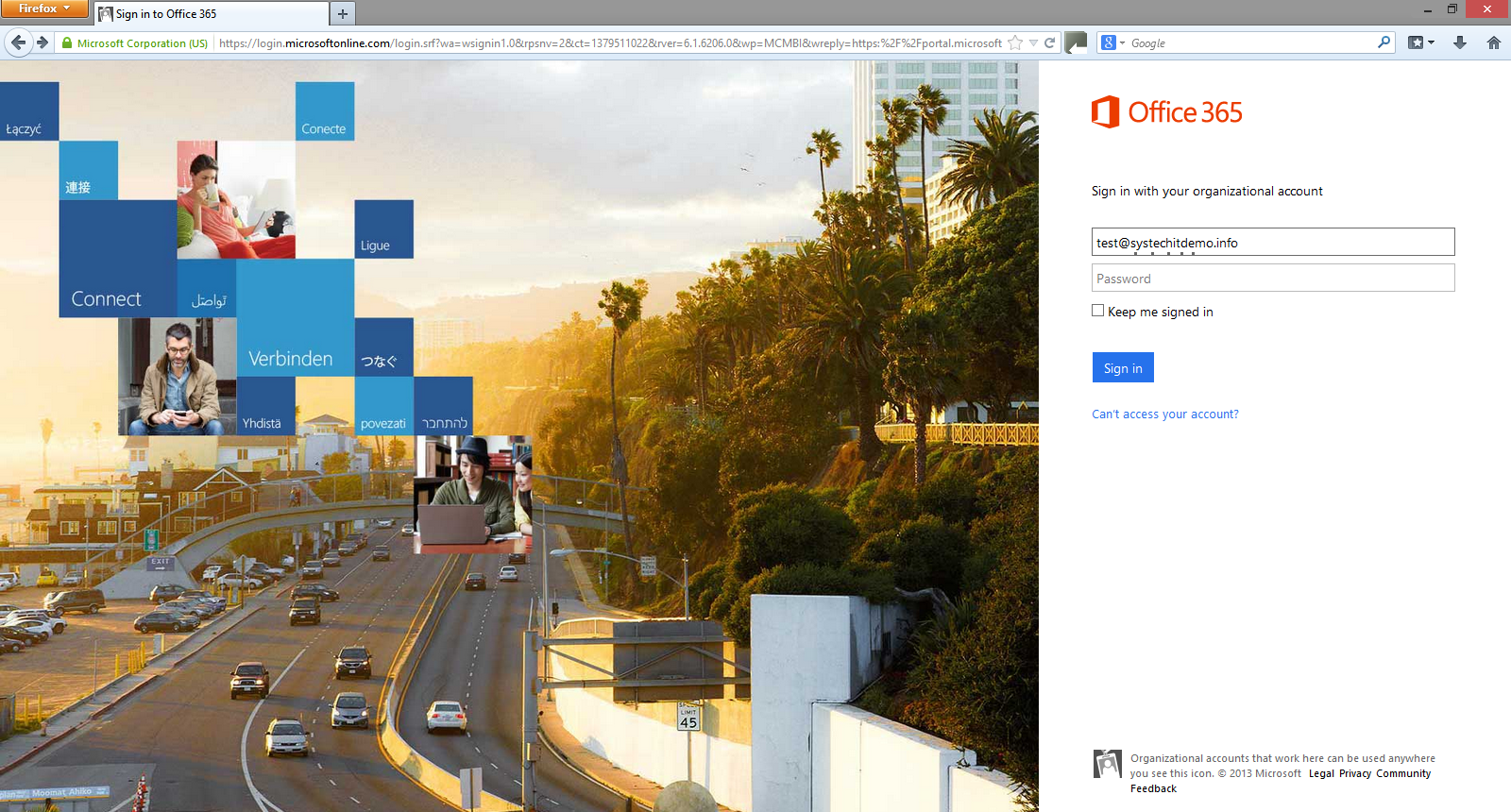 ](
](
[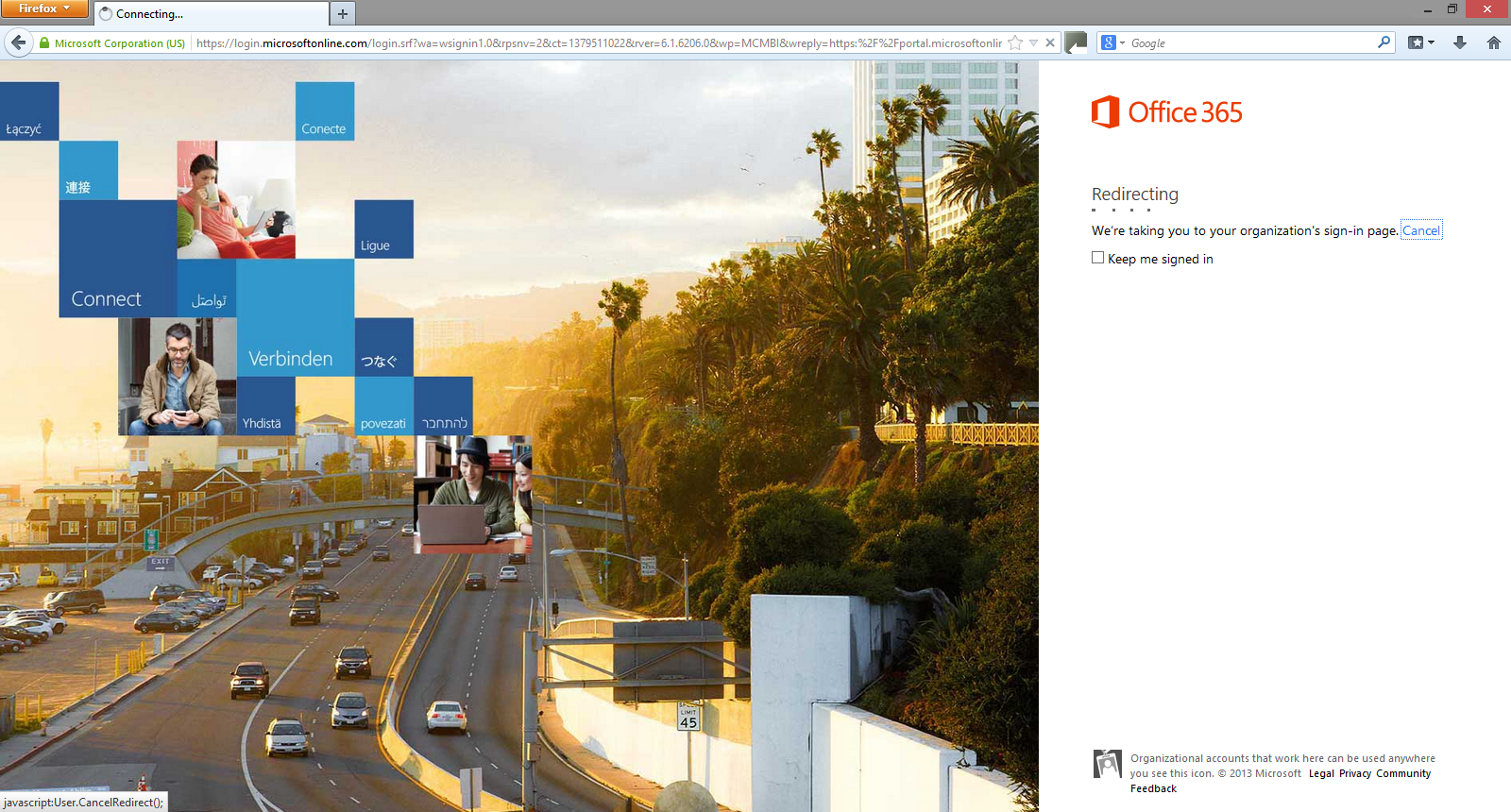 ](
](
[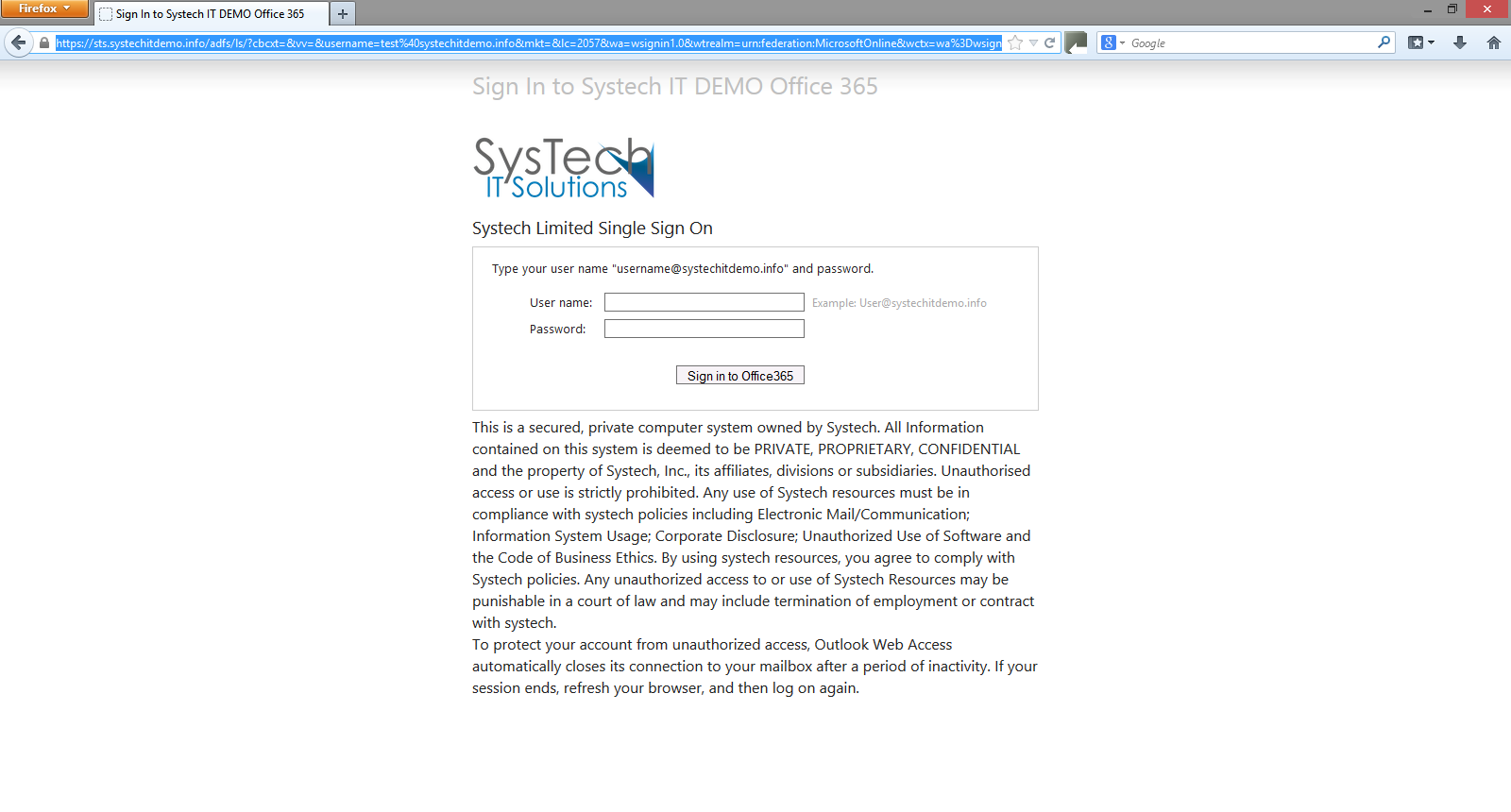 ](
](
